
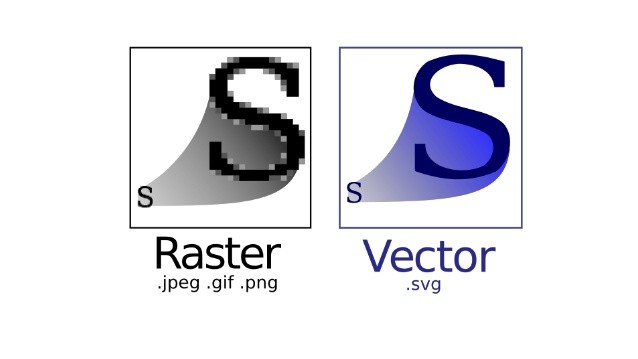
四种常见的图像格式:
GIF:图像互换格式
JPEG:联合图像专家组

PNG:可移植网络图形格式

SVG:可缩放矢量图形

不同文件格式的适用情境:
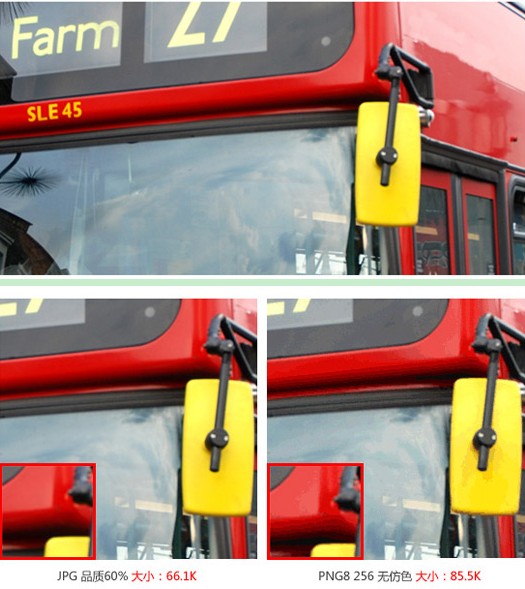
什么时候应该使用JPEG?

什么时候应该使用PNG?

什么时候使用SVG?
当你年老时,你是否常常想,要是年轻时多努力下该好。








让我们先来了解一下端口转发的概念吧。我们知道,SSH 会自动加密和解密所有 SSH 客户端与服务端之间的网络数据。但是,SSH 还同时提供了一个非常有用的功能,这就是端口转发。它能够将其他 TCP 端口的网络数据通过 SSH 链接来转发,并且自动提供了相应的加密及解密服务。这一过程有时也被叫做“隧道”(tunneling),这是因为 SSH 为其他 TCP 链接提供了一个安全的通道来进行传输而得名。例如,Telnet,SMTP,LDAP 这些 TCP 应用均能够从中得益,避免了用户名,密码以及隐私信息的明文传输。而与此同时,如果您工作环境中的防火墙限制了一些网络端口的使用,但是允许 SSH 的连接,那么也是能够通过将 TCP 端口转发来使用 SSH 进行通讯。总的来说 SSH 端口转发能够提供两大功能:
1、加密 SSH Client 端至 SSH Server 端之间的通讯数据。
2、突破防火墙的限制完成一些之前无法建立的 TCP 连接。
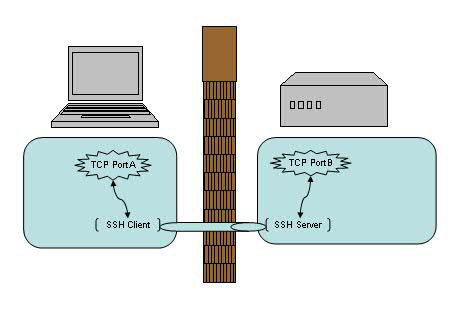
如上图所示,使用了端口转发之后,TCP 端口 A 与 B 之间现在并不直接通讯,而是转发到了 SSH 客户端及服务端来通讯,从而自动实现了数据加密并同时绕过了防火墙的限制。
在选择端口号时要注意非管理员帐号是无权绑定 1-1023 端口的,所以一般是选用一个 1024-65535 之间的并且尚未使用的端口号即可。
假设:
墙内客户端 A 128.128.128.128
墙外代理服务器 B 138.138.138.138
目标服务器 C 158.158.158.158
如果 A不能直接访问C ,B能访问C , A能访问B。
可以采用 本地端口转发:
绑定A上的一个端口如2233 ,A向B发起建立SSH隧道连接请求,然后B再访问 C上的端口如5566
这样:访问A上的2233端口 就等于 在访问 C上5566端口
# root@root@B的IP地址 以root用户 登录 B 服务器 #-v 冗详模式. 使打印关于运行情况的调试信息. 在调试连接, 认证和配置问题时非常有用. #并联的 -v 选项能够增加冗详程度. 最多为三个. #-C 要求进行数据压缩 (包括 stdin, stdout, stderr以及转发X11和TCP/IP连接的数据) #-L port:host:hostport 将本地机[主机A]的某个端口[port]转发到远端指定机器[主机C别名host]的指定端口[hostport] # 工作原理是这样的,本地机器[主机A]上分配了一个 socket 侦听 port 端口, 一旦这个端口上有了连接, # 该连接就经过安全通道转发出去, 同时远程主机[主机B]和 host[主机C] 的 hostport 端口建立连接. # 可以在配置文件中指定端口的转发. 只有 root 才能转发特权端口. IPv6 地址用另一种格式说明: port/host/hostport ssh -v -C -L 2233:C的IP地址:5566 root@B的IP地址 -p B的ssh端口号
那么这个端口转发可以被其他机器使用么?比如能否新增加一台 [主机X] 来直接连接 [主机A] 的 2233 端口?答案是不行的,在主流 SSH 实现中,本地端口转发绑定的是 lookback 接口,这意味着只有 localhost 或者 127.0.0.1 才能使用本机的端口转发 , 其他机器发起的连接只会得到“ connection refused. ”。好在 SSH 同时提供了 GatewayPorts 关键字,我们可以通过指定它与其他机器共享这个本地端口转发。
ssh -g -L 主机A的端口如5901:主机C:主机C的端口如5901 通过SSH连接的主机B
特殊情况下:C的IP地址:5566 可以变成 localhost:5566
localhost:5566 是针对 中间的代理服务器 来说的
这相当于A访问自己的2233端口时 等价于 直接访问B内部的5566端口[若5566端口没有暴露给别的主机,就可规避B上的防火墙]
ssh -v -C -L 2233:localhost:5566 root@B的IP地址 -p B的ssh端口号
假设:
墙内客户端 A 128.128.128.128
墙外代理服务器 B 138.138.138.138
目标服务器 C 158.158.158.158
如果 A不能直接访问C ,B能访问C , B能访问A。
可以采用 远程端口转发:
绑定A上的一个端口如2233 ,B向A发起建立SSH隧道连接请求,然后B再访问C上的端口如5566
这样:访问A上的2233端口 就等于 在访问 C上5566端口
#-R port:host:hostport 将客户机[主机A]的某个端口[port]转发到远端指定机器[主机C别名host]的指定端口[hostport] # 工作原理是这样的, 远程主机[主机A]上分配了一个 socket 侦听 port 端口, 一旦这个端口上有了连接, # 该连接就经过安全通道转向出去, 同时本地主机[主机B]和 host[主机C] 的 hostport 端口建立连接. # 可在配置文件中指定端口的转发.只有root登录远程主机[主机A]才能转发特权端口. # IPv6 地址用另一种格式说明: port/host/hostport ssh -v -C -R 2233:C的IP地址:5566 root@A的IP地址 -p A的ssh端口号
特殊情况下:C的IP地址:5566 可以变成 localhost:5566
localhost:5566 是针对 中间的代理服务器 来说的
这相当于A访问自己的2233端口时 等价于 直接访问B内部的5566端口[若5566端口没有暴露给别的主机,就可规避B上的防火墙]
ssh -v -C -R 2233:localhost:5566 root@A的IP地址 -p A的ssh端口号
总之,port:host:hostport 这三个参数,是按照,实际操作中,谁是代理服务器,来进行区分配置的。
恩,动态转发,听上去很酷。当你看到这里时,有没有想过我们已经讨论过了本地转发,远程转发,但是前提都是要求有一个固定的应用服务端的端口号,例如前面例子中的 主机C 的 5566 端口。那如果没有这个端口号怎么办?等等,什么样的应用会没有这个端口号呢?嗯,比如说用浏览器进行 Web 浏览,比如说 MSN 等等。
当我们在一个不安全的 WiFi 环境下上网,用 SSH 动态转发来保护我们的网页浏览及 MSN 信息无疑是十分必要的。让我们先来看一下动态转发的命令格式:
|
1
|
$ ssh -D <local port> <SSH Server> |
例如:
|
1
|
$ ssh -D 7001 <SSH Server> |
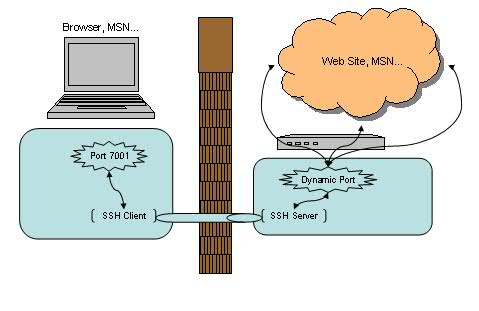
似乎很简单,我们选择了 7001 作为本地的端口号,其实在这里 SSH 是创建了一个 SOCKS 代理服务。来看看帮助文档中对 -D 参数的描述:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
-D port This works by allocating a socket to listen to port on the local side, and whenever a connection is made to this port, the con- nection is forwarded over the secure channel, and the applica- tion protocol is then used to determine where to connect to from the remote machine. Currently the SOCKS4 and SOCKS5 protocols are supported, and ssh will act as a SOCKS server. Only root can forward privileged ports. Dynamic port forwardings can also be specified in the configuration file. |
之后的使用就简单了,我们可以直接使用 localhost:7001 来作为正常的 SOCKS 代理来使用,直接在浏览器或 MSN 上设置即可。在 SSH Client 端无法访问的网站现在也都可以正常浏览。而这里需要值得注意的是,此时 SSH 所包护的范围只包括从浏览器端(SSH Client 端)到 SSH Server 端的连接,并不包含从 SSH Server 端 到目标网站的连接。如果后半截连接的安全不能得到充分的保证的话,这种方式仍不是合适的解决方案。
好了,让我们来看最后一个例子 – X 协议转发。
我们日常工作当中,可能会经常会远程登录到 Linux/Unix/Solaris/HP 等机器上去做一些开发或者维护,也经常需要以 GUI 方式运行一些程序,比如要求图形化界面来安装 DB2/WebSphere 等等。这时候通常有两种选择来实现:VNC 或者 X 窗口,让我们来看看后者。
使用 X 窗口通常需要分别安装:X Client 和 X Server 。在本例中我们的 X Client 就是所访问的远程 Linux/Unix/Solaris/HP,而我们的 X Server 则是发起访问的本地机器(例如你面前正在使用的笔记本或台式机)。把 X Client 端的 X 窗口显示在 X Server 端需要先行在 X Client 端指定 X Server 的位置,命令格式如下:
|
1
|
export DISPLAY=<X Server IP>:<display #>.<virtual #> |
例如:
|
1
|
export DISPLAY=myDesktop:1.0 |
然后直接运行 X 应用即可,X 窗口就会自动在我们的本地端打开。
一切运行正常,但是,这时候 IT 部门突然在远程 Linux/Unix/Solaris/HP 前面加了一道防火墙。非常不幸的是,X 协议并不在允许通过的列表之内。怎么办?只能使用 VNC 了么?不,其实只要使用了 SSH 端口转发即可通过,同时也对 X 通讯数据做了加密,真是一举两得。(当然,使用此方法前最好先咨询相关 IT 部门是否符合相应的安全条例,以免造成违规操作。)
建立命令也很简单,直接从本地机器(X Server 端)发起一个如下的 SSH 连接即可:
|
1
|
$ ssh -X <SSH Server> |
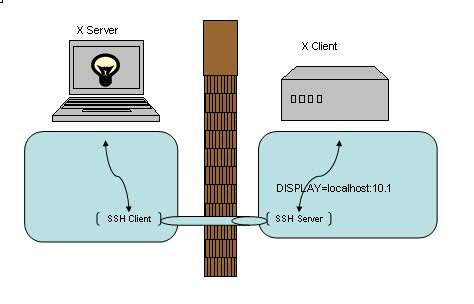
建立连接之后就可以直接运行远程的 X 应用。注意建立 X 转发之后会自动设置 DISPLAY 环境变量,通常会被设置成localhost:10.0,我们无需也不应该在连接之后再进行修改此环境变量。
一个比较常见的场景是,我们的本地机器是 Windows 操作系统,这时可以选择开源的 XMing 来作为我们的 XServer,而 SSH Client 则可以任意选择了,例如 PuTTY,Cygwin 均可以配置 访问 SSH 的同时建立 X 转发。
至此,我们已经完成了本地端口转发,远程端口转发,动态端口转发以及 X 转发的介绍。回顾起来,总的思路是通过将 TCP 连接转发到 SSH 通道上以解决数据加密以及突破防火墙的种种限制。对一些已知端口号的应用,例如 Telnet/LDAP/SMTP,我们可以使用本地端口转发或者远程端口转发来达到目的。动态端口转发则可以实现 SOCKS 代理从而加密以及突破防火墙对 Web 浏览的限制。对于 X 应用,无疑是 X 转发最为适用了。虽然每一部分我们都只是简单的介绍了一下,但如果能灵活应用这些技巧,相信对我们的日常生活 / 工作也是会有所帮助的。
如果 由于网络和谐,SSH 无法连接到远程服务器(time out 神马的),可以设置代理服务器。
找到ssh的配置文件。(可能需要自己手动创建txt文件,文件全名:config)
socket 代理 软件 配置
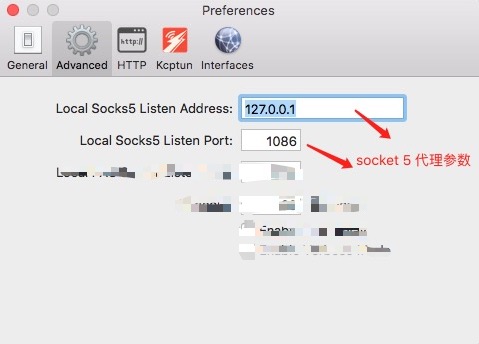
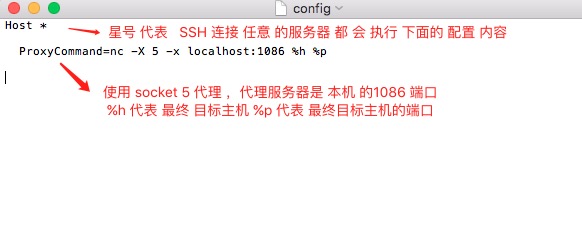
可复制以下代码到文件 ~/.ssh/config
Host * ProxyCommand=nc -X 5 -x localhost:1086 %h %p
配置: ProxyCommand ,总得来说代理 方式 大致可分为两种。 参数 %h 指最终目标主机 %p 指最终目标主机端口
一、在客户端主机 和 中间人主机 上面 建立起 SSH隧道,然后通过操作中间人主机 通过SSH 远程登录目标主机。
举例:
+-------+ +----------+ +-----------+
| Laptop| <---> | Jumphost | <--> | FooServer |
+-------+ +----------+ +-----------+
OR
+-------+ +----------+ +-----------+
| Laptop| <---> | Firewall | <--> | FooServer |
+-------+ +----------+ +-----------+
192.168.1.5 121.1.2.3 10.10.29.68
直接尝试 连续登录 两个服务器。
I can can only access a remote server named ‘FooServer’ via ssh by first login into an intermediary server called ‘Jumphost’.
First, login to Jumphost:
$ ssh vivek@Jumphost
Next, I must ssh through the intermediary system as follows:
$ ssh vivek@FooServer
Instead of typing two ssh command, I can type the following all-in-one command. This is useful for connecting to FooServer via firewall called ‘Jumphost’ as the jump host:
$ ssh -tt Jumphost ssh -tt FooServer $ ssh -tt vivek@Jumphost ssh -tt vivek@FooServer # 下面这句 command1 代表的是 登录终端服务器后,就直接进行的 shell 命令 command1 $ ssh -tt vivek@Jumphost ssh -tt vivek@FooServer command1 arg1 arg2 # Run htop over ssh via single command # ssh [email protected] 'htop' # Error opening terminal: unknown. # Use the -t flag with SSH; test OK ! # This will force a TTY allocation (ssh doesn't allocate a TTY if it's not necessary, normally only for interactive shells). # ssh [email protected] -t 'htop' $ ssh -tt vivek@Jumphost ssh -tt vivek@FooServer htop $ ssh -tt vivek@Jumphost ssh -tt vivek@FooServer screen -dR
-t option passed to the ssh command force pseudo-tty allocation. This can be used to execute arbitrary screen-based programs on a remote machine. Multiple -tt options force tty allocation, even if ssh has no local tty. -t 强制分配伪终端. 可以在远程机器上执行任何全屏幕(screen-based)程序, 所以非常有用, 例如菜单服务. 并联的 -t 选项强制分配终端, 即使 没有本地终端.
更好的办法是 调用 命令 ProxyCommand
$ ssh -o ProxyCommand='ssh vivek@Jumphost nc FooServer 22' vivek@FooServer ########################################## ## -t option is needed to run commands ### ########################################## $ ssh -t -o ProxyCommand='ssh vivek@Jumphost nc FooServer 22' vivek@FooServer htop
The netcat (nc) command is needed to set and establish a TCP pipe between Jumphost (or firewall) and FooServer. Now, my laptop (local system) is connected to Jumphost it now connected FooServer. In this example, the utility netcat (nc) is for reading and writing network connections directly. It can be used to pass connections to a 2nd server such as FooServer.
或者使用 配置文件
# Edit the $HOME/.ssh/config file using a text editor such as vim, enter: $ vim ~/.ssh/config
# Append the following configuration: Host fooserver #(随便取一个[昵称名] , 用户 客户端 直接 ssh [昵称名]) HostName FooServer #(远程目标主机) User vivek #(远程目标主机登入用户名) ProxyCommand ssh vivek@Jumphost nc %h %p
Save and close the file. Where,
1.Host fooserver : Set nickname of your choice.
2.HostName FooServer : Set the real remote server/host name.
3.User vivek : Set the real user name for remote server/host.
4.ProxyCommand ssh vivek@Jumphost nc %h %p : Specifies the command to use to connect to the server. In this example, I’m using nc command. Any occurrence of %h will be substituted by the host name to connect, %p by the port, and %r by the remote user name.
To test enter:
$ ssh fooserver
To see the details, pass the -v option to the ssh command. Here is another snippet:
Host server1 HostName v.server1 User root Port 22 ProxyCommand ssh [email protected] nc %h %p %r
Now, run:
$ ssh -v server1
Sample outputs:
OpenSSH_6.2p2, OSSLShim 0.9.8r 8 Dec 2011 debug1: Reading configuration data /Users/veryv/.ssh/config debug1: /Users/veryv/.ssh/config line 1: Applying options for server1 debug1: Reading configuration data /etc/ssh_config debug1: /etc/ssh_config line 20: Applying options for * debug1: /etc/ssh_config line 102: Applying options for * debug1: Executing proxy command: exec ssh [email protected] nc v.server1 22 root ................
On the outside (ssh -W uses a special channel rather than using a normal session channel), it is equivalent to ssh’ing to the ssh_jump_host and calling netcat:
# 下面的两条命令 其实是 差不多的 ,只是 -W 建立的隧道不是普通的 SSH 隧道罢了 ProxyCommand ssh ssh_jump_host "nc %h %p" ProxyCommand ssh -W %h:%p ssh_jump_host
其他补充:
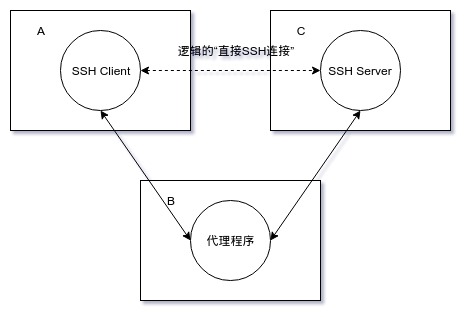
ProxyCommand 选项值形式为
ssh -W C:CPort -l USER -i PRIVATE_KEY -p BPort B
原理:ssh命令自提供的代理机制,在机器A上 建立与B的SSH连接
(使用”-l USER -i PRIVATE_KEY -p BPort B”这些参数)
该SSH连接的B端侧与机器C上的SSH Server端口(即“C:CPort”)建立连接,
该SSH连接的A端侧与机器A上的SSH Client
(即“最终欲建立‘间接SSH连接’在机器A上的SSH Client”)建立连接。
假定A上ssh_config配置文件内容如下:
Host B
HostName %h
User dsl
Port 1046
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_dsa
Host C
HostName %h
User dsl
Port 1046
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
ProxyCommand ssh -W %h:%p B
在A上执行ssh C命令,发现A与C成功建立SSH连接。根据以上所述,此时在A上应该有两个SSH进程,一个对应于“A与B的SSH连接”,另外一个对应于“A与C的SSH连接”。在A上执行ps -ef | grep ‘ssh’命令,得到如下结果,得证。
7851 7689 15:55 S pts/10 ssh C 7852 7851 15:55 S pts/10 ssh -W C:1046 B
二、利用外界现有的代理服务器。
“ProxyCommand”选项值形式为“nc -X 5 -x B:BPort C CPort”,
原理:利用“nc”命令,在机器A上使用“nc”命令与代理服务器
(即“-x B:BPort”,通过“-X 5”参数来指定与代理服务器的通信协议为“SOCKS4/SOCKS5/HTTPS”)建立代理连接,
该代理服务器连接的B端侧与机器C上的SSH Server端口(即“C CPort”)建立连接,
该代理服务器连接的A端侧与机器A上的SSH Client
(即“最终欲建立‘间接SSH连接’在机器A上的SSH Client”)建立连接。
假定A上ssh_config配置文件内容如下:
Host C
HostName %h
User dsl
Port 1046
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
ProxyCommand nc -X 5 -x B:8989 %h %p
在A上执行ssh C命令,发现A与C成功建立SSH连接。根据以上所述,此时在A上应该有一个NC进程和一个SSH进程,前者对应于“A与B的代理连接”,后者对应于“A与C的SSH连接”。在A上执行ps -ef | grep -e ‘ssh’ -e ‘nc’命令,得到如下结果,得证。
8816 8089 16:08 S pts/10 ssh C 8817 8816 16:08 S pts/10 nc -X 5 -x B:8989 C 1046
ProxyCommand -X 参数含义 -x 参数含义 :
-X proxy_protocol Requests that nc should use the specified protocol when talking to the proxy server. Supported protocols are “4” (SOCKS v.4), “5” (SOCKS v.5) and “connect” (HTTPS proxy). If the protocol is not specified, SOCKS version 5 is used. -x proxy_address[:port] Requests that nc should connect to destination using a proxy at proxy_address and port. If port is not specified, the well-known port for the proxy protocol is used (1080 for SOCKS, 3128 for HTTPS). An IPv6 address can be specified unambiguously by enclosing proxy_address in square brackets.
补充:关于SSH配置的问题:
ssh_config(5)
~/.ssh/config This is the per-user configuration file. The file format and configuration options are described in ssh_config(5). Because of the potential for abuse, this file must have strict permissions: read/write for the user, and not writable by others. /etc/ssh/ssh_config Systemwide configuration file. The file format and configuration options are described in ssh_config(5).
补充更新:
centos更新openssh后不再支持ssh 第一版协议,所以第一版协议的配置信息也不需要了。
#这些配置信息都属于第一版协议,现在已经不需要了。 RSAAuthentication yes #指定公钥数据库文件 AuthorsizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys
提示:
密钥会生成两个文件 [私钥 (id_rsa) 与公钥 (id_rsa.pub)] ,建议设置并牢记passphrase密码短语。
Linux:
ssh-keygen -t rsa
Windows:SecurCRT/Xshell/PuTTY
SSH-2 RSA 2048
一、创建密钥
#生成SSH密钥对 ssh-keygen -t rsa Generating public/private rsa key pair. #建议直接回车使用默认路径 Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): #输入密码短语(留空则直接回车) Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): #重复密码短语 Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: aa:8b:61:13:38:ad:b5:49:ca:51:45:b9:77:e1:97:e1 [email protected] The key's randomart image is: +--[ RSA 2048]----+ | .o. | | .. . . | | . . . o o | | o. . . o E | |o.= . S . | |.*.+ . | |o.* . | | . + . | | . o. | +-----------------+
二、复制密钥对
#复制公钥到无密码登录的服务器上,22端口改变可以使用下面的命令
#ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub “-p 10022 user@server”
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
或者也可以手动在服务器端建立目录和authorized_keys,注意修改权限。
也或者, you can paste in the keys using SSH (下面是一行命令)
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh [email protected] "mkdir -p ~/.ssh && cat >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys"
No matter which command you chose, you should see something like:
The authenticity of host ‘12.34.56.78 (12.34.56.78)’ can’t be established.
RSA key fingerprint is b1:2d:33:67:ce:35:4d:5f:f3:a8:cd:c0:c4:48:86:12.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added ‘12.34.56.78’ (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
[email protected]’s password:
Now try logging into the machine, with “ssh ‘[email protected]′”, and check in:
~/.ssh/authorized_keys
to make sure we haven’t added extra keys that you weren’t expecting.
三、修改SSH配置文件 (测试效果 成功)
提示:
1、RSAAuthentication yes;这个配置好像没有了
2、PermitRootLogin yes; 表示 root 用户 可以 通过 SSH 登录:不是一定要修改的。
#编辑sshd_config文件 vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config #禁用密码验证 PasswordAuthentication no #启用密钥验证 RSAAuthentication yes PubkeyAuthentication yes #指定公钥数据库文件 AuthorsizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys
其实可以直接用命令行 来修改 ssh 的配置值。
sed -i "s/^PasswordAuthentication.*/PasswordAuthentication no/g" /etc/ssh/sshd_config sed -i "s/^#RSAAuthentication.*/RSAAuthentication yes/g" /etc/ssh/sshd_config sed -i "s/^#PubkeyAuthentication.*/PubkeyAuthentication yes/g" /etc/ssh/sshd_config sed -i "s/^#AuthorizedKeysFile.*/AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh\/authorized_keys/g" /etc/ssh/sshd_config
centos 下:
首先修改配置文件 vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
(注意 网页 复制代码的 时候 vim和/etc中间的 空格有问题,导致shell 终端 无法识别 vim空格 命令)
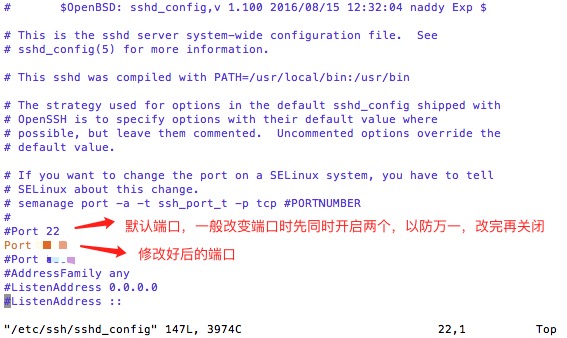
重新总结一下:
step1 修改/etc/ssh/sshd_config
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
#Port 22 //这行去掉#号
Port 20000 //下面添加这一行
step2 修改SELinux
(这一步 centos 好像 不需要啊,有些版本好像还是需要的)
另外需要注意一点就是,如果selinux没有关闭,那么端口会绑定失败, 使用 systemctl status sshd.service 命令查看状态时 会发现error: Bind to port 2223 on 0.0.0.0 failed: Permission denied,的错误, 这种情况改下,要关闭selinux,然后再次重新启动ssh服务,新的端口才可以生效
如果忽略这一步,发现端口修改无效,可以看看systemctl status sshd.service
semanage 命令如果找不到,
-bash: semanage: command not found
就先查找,哪个软件提供这条命令
yum provides /usr/sbin/semanage # 也可以用 下面这条命令 yum whatprovides /usr/sbin/semanage
可能输出:
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Determining fastest mirrors * base: mirror.nbrc.ac.in * extras: mirror.nbrc.ac.in * updates: mirror.nbrc.ac.in policycoreutils-python-2.2.5-11.el7.x86_64 : SELinux policy core python : utilities Repo : base Matched from: Filename : /usr/sbin/semanage policycoreutils-python-2.2.5-11.el7_0.1.x86_64 : SELinux policy core python : utilities Repo : updates Matched from: Filename : /usr/sbin/semanage
As you see in the above output, we need to install the package policycoreutils-python-2.2.5-11.el7_0.1.x86_64 in order to use ‘semanage’ command.
so, let us install policycoreutils-python-2.2.5-11.el7_0.1.x86_64 package using command:
yum install policycoreutils-python
使用以下命令查看当前SElinux 允许的ssh端口:
semanage port -l | grep ssh
添加20000端口到 SELinux
semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 20000
然后确认一下是否添加进去
semanage port -l | grep ssh
如果成功会输出
ssh_port_t tcp 20000, 22
step3 重启ssh
systemctl restart sshd.service
step4 配置防火墙端口号
centos7 防火墙 改成了 firewalld 替换 原来的 iptable 了。
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=12588/tcp (ssh改用的端口号) firewall-cmd --reload(重新加载防火墙配置) 因为 ssh 默认端口改了 所以 开放 ssh 使用 的端口吧 (结果没有用) firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service ssh
课外补充: 使用 防火墙 屏蔽 ip 地址
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family='ipv4' source address='128.128.128.128' reject"
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/freeweb/p/5667166.html
Linux Troubleshooting – semanage command not found in CentOS 7/RHEL 7
查看SSH服务是否开启
[root@localhost ~]# sudo ps -e | grep ssh 1128 ? 00:00:00 sshd [root@localhost ~]#
如果没有反应或者其他结果,再试着开启SSH服务。
使用命令 sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start来开启服务
如果没有安装SSH服务,此时需要安装 SSH服务。
yum install openssh-server -y
启动sshd服务
如果没有启动,则需要启动该服务: systemctl start sshd.service 其实.service可不写,直接 systemctl restart sshd 重启 sshd 服务: systemctl restart sshd.service 设置服务开启自启: systemctl enable sshd.service
使用ssh
### -p 后面是端口号 | 再后面是 用户名@服务器地址 | -v 是 输出连接信息,方便查找连接失败原因 ssh -p 22 [email protected] -v
mac下利用 终端 Terminal ,调用 shell 的新建远程 连接 方法,进行 SSH 连接。
普通连接方式:
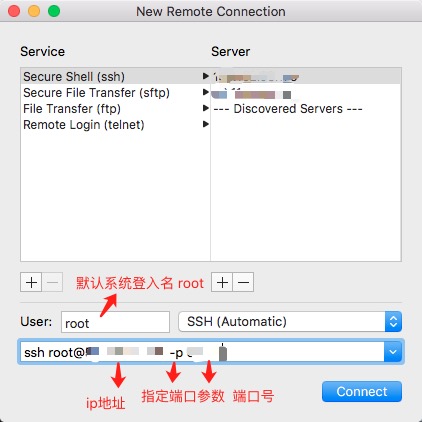
直接用 ssh 登录 远程服务器
# root是远程服务器的默认管理员账户,所以用root登录,登录完成后,可以分配其他用户账号。 # 128.128.128.128 是远程 服务器ip地址 # -p 是指定 远程ssh服务器 端口后,默认22端口,如果 不是22 端口 需要设置 -p 参数 # -v 是打印 ssh 运行过程中的 日志文件,方便发现错误,可以不设置 ssh [email protected] -p 12880 -v
也可以参看:
https://www.cnblogs.com/ftl1012/p/ssh.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/jiarenanhao/p/9938280.html
ssh — OpenSSH SSH client (remote login program)
| ssh | [-46AaCfGgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy] [-b bind_address] [-c cipher_spec] [-D[bind_address:]port] [-E log_file] [-e escape_char] [-F configfile] [-I pkcs11] [-iidentity_file] [-J destination] [-L address] [-l login_name] [-m mac_spec] [-O ctl_cmd] [-ooption] [-p port] [-Q query_option] [-R address] [-S ctl_path] [-W host:port] [-wlocal_tun[:remote_tun]] destination [command] |
ssh (SSH client) is a program for logging into a remote machine and for executing commands on a remote machine. It is intended to provide secure encrypted communications between two untrusted hosts over an insecure network. X11 connections, arbitrary TCP ports and UNIX-domain sockets can also be forwarded over the secure channel.
ssh connects and logs into the specified destination, which may be specified as either [user@]hostname or a URI of the form ssh:// [user@]hostname[:port]. The user must prove his/her identity to the remote machine using one of several methods (see below).
If a command is specified, it is executed on the remote host instead of a login shell.
The options are as follows:
Agent forwarding should be enabled with caution. Users with the ability to bypass file permissions on the remote host (for the agent’s UNIX-domain socket) can access the local agent through the forwarded connection. An attacker cannot obtain key material from the agent, however they can perform operations on the keys that enable them to authenticate using the identities loaded into the agent.
IPv6 addresses can be specified by enclosing the address in square brackets. Only the superuser can forward privileged ports. By default, the local port is bound in accordance with the GatewayPorts setting. However, an explicitbind_address may be used to bind the connection to a specific address. Thebind_address of “localhost” indicates that the listening port be bound for local use only, while an empty address or ‘*’ indicates that the port should be available from all interfaces.
~’). The escape character is only recognized at the beginning of a line. The escape character followed by a dot (‘.’) closes the connection; followed by control-Z suspends the connection; and followed by itself sends the escape character once. Setting the character to “none” disables any escapes and makes the session fully transparent.If the ExitOnForwardFailure configuration option is set to “yes”, then a client started with -f will wait for all remote port forwards to be successfully established before placing itself in the background.
Port forwardings can also be specified in the configuration file. Only the superuser can forward privileged ports. IPv6 addresses can be specified by enclosing the address in square brackets.
By default, the local port is bound in accordance with the GatewayPorts setting. However, an explicit bind_address may be used to bind the connection to a specific address. The bind_address of “localhost” indicates that the listening port be bound for local use only, while an empty address or ‘*’ indicates that the port should be available from all interfaces.
AddKeysToAgent AddressFamily BatchMode BindAddress CanonicalDomains CanonicalizeFallbackLocal CanonicalizeHostname CanonicalizeMaxDots CanonicalizePermittedCNAMEs CertificateFile ChallengeResponseAuthentication CheckHostIP Ciphers ClearAllForwardings Compression ConnectionAttempts ConnectTimeout ControlMaster ControlPath ControlPersist DynamicForward EscapeChar ExitOnForwardFailure FingerprintHash ForwardAgent ForwardX11 ForwardX11Timeout ForwardX11Trusted GatewayPorts GlobalKnownHostsFile GSSAPIAuthentication GSSAPIDelegateCredentials HashKnownHosts Host HostbasedAuthentication HostbasedKeyTypes HostKeyAlgorithms HostKeyAlias HostName IdentitiesOnly IdentityAgent IdentityFile Include IPQoS KbdInteractiveAuthentication KbdInteractiveDevices KexAlgorithms LocalCommand LocalForward LogLevel MACs Match NoHostAuthenticationForLocalhost NumberOfPasswordPrompts PasswordAuthentication PermitLocalCommand PKCS11Provider Port PreferredAuthentications ProxyCommand ProxyJump ProxyUseFdpass PubkeyAcceptedKeyTypes PubkeyAuthentication RekeyLimit RemoteCommand RemoteForward RequestTTY SendEnv ServerAliveInterval ServerAliveCountMax StreamLocalBindMask StreamLocalBindUnlink StrictHostKeyChecking TCPKeepAlive Tunnel TunnelDevice UpdateHostKeys UsePrivilegedPort User UserKnownHostsFile VerifyHostKeyDNS VisualHostKey XAuthLocation
This works by allocating a socket to listen to either a TCP port or to a Unix socket on the remote side. Whenever a connection is made to this port or Unix socket, the connection is forwarded over the secure channel, and a connection is made from the local machine to either an explicit destination specified by host porthostport, or local_socket, or, if no explicit destination was specified, ssh will act as a SOCKS 4/5 proxy and forward connections to the destinations requested by the remote SOCKS client.
Port forwardings can also be specified in the configuration file. Privileged ports can be forwarded only when logging in as root on the remote machine. IPv6 addresses can be specified by enclosing the address in square brackets.
By default, TCP listening sockets on the server will be bound to the loopback interface only. This may be overridden by specifying a bind_address. An emptybind_address, or the address ‘*’, indicates that the remote socket should listen on all interfaces. Specifying a remote bind_address will only succeed if the server’s GatewayPorts option is enabled (see sshd_config(5)).
If the port argument is ‘0’, the listen port will be dynamically allocated on the server and reported to the client at run time. When used together with -O forward the allocated port will be printed to the standard output.
The devices may be specified by numerical ID or the keyword “any”, which uses the next available tunnel device. If remote_tun is not specified, it defaults to “any”. See also the Tunnel and TunnelDevice directives in ssh_config(5). If theTunnel directive is unset, it is set to the default tunnel mode, which is “point-to-point”.
X11 forwarding should be enabled with caution. Users with the ability to bypass file permissions on the remote host (for the user’s X authorization database) can access the local X11 display through the forwarded connection. An attacker may then be able to perform activities such as keystroke monitoring.
For this reason, X11 forwarding is subjected to X11 SECURITY extension restrictions by default. Please refer to the ssh -Y option and the ForwardX11Trusted directive in ssh_config(5) for more information.
ssh may additionally obtain configuration data from a per-user configuration file and a system-wide configuration file. The file format and configuration options are described inssh_config(5).
The OpenSSH SSH client supports SSH protocol 2.
The methods available for authentication are: GSSAPI-based authentication, host-based authentication, public key authentication, challenge-response authentication, and password authentication. Authentication methods are tried in the order specified above, thoughPreferredAuthentications can be used to change the default order.
Host-based authentication works as follows: If the machine the user logs in from is listed in /etc/hosts.equiv or /etc/shosts.equiv on the remote machine, and the user names are the same on both sides, or if the files ~/.rhosts or ~/.shosts exist in the user’s home directory on the remote machine and contain a line containing the name of the client machine and the name of the user on that machine, the user is considered for login. Additionally, the server must be able to verify the client’s host key (see the description of /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hostsand ~/.ssh/known_hosts, below) for login to be permitted. This authentication method closes security holes due to IP spoofing, DNS spoofing, and routing spoofing. [Note to the administrator: /etc/hosts.equiv, ~/.rhosts, and the rlogin/rsh protocol in general, are inherently insecure and should be disabled if security is desired.]
Public key authentication works as follows: The scheme is based on public-key cryptography, using cryptosystems where encryption and decryption are done using separate keys, and it is unfeasible to derive the decryption key from the encryption key. The idea is that each user creates a public/private key pair for authentication purposes. The server knows the public key, and only the user knows the private key. ssh implements public key authentication protocol automatically, using one of the DSA, ECDSA, Ed25519 or RSA algorithms. The HISTORY section of ssl(8) contains a brief discussion of the DSA and RSA algorithms.
The file ~/.ssh/authorized_keys lists the public keys that are permitted for logging in. When the user logs in, the ssh program tells the server which key pair it would like to use for authentication. The client proves that it has access to the private key and the server checks that the corresponding public key is authorized to accept the account.
The server may inform the client of errors that prevented public key authentication from succeeding after authentication completes using a different method. These may be viewed by increasing the LogLevel to DEBUG or higher (e.g. by using the -v flag).
The user creates his/her key pair by running ssh-keygen(1). This stores the private key in ~/.ssh/id_dsa (DSA), ~/.ssh/id_ecdsa (ECDSA), ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 (Ed25519), or~/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA) and stores the public key in ~/.ssh/id_dsa.pub (DSA),~/.ssh/id_ecdsa.pub (ECDSA), ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub (Ed25519), or ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub(RSA) in the user’s home directory. The user should then copy the public key to~/.ssh/authorized_keys in his/her home directory on the remote machine. The authorized_keys file corresponds to the conventional ~/.rhosts file, and has one key per line, though the lines can be very long. After this, the user can log in without giving the password.
A variation on public key authentication is available in the form of certificate authentication: instead of a set of public/private keys, signed certificates are used. This has the advantage that a single trusted certification authority can be used in place of many public/private keys. See the CERTIFICATES section of ssh-keygen(1) for more information.
The most convenient way to use public key or certificate authentication may be with an authentication agent. See ssh-agent(1) and (optionally) the AddKeysToAgent directive inssh_config(5) for more information.
Challenge-response authentication works as follows: The server sends an arbitrary “challenge” text, and prompts for a response. Examples of challenge-response authentication include BSD Authentication (see login.conf(5)) and PAM (some non-OpenBSD systems).
Finally, if other authentication methods fail, ssh prompts the user for a password. The password is sent to the remote host for checking; however, since all communications are encrypted, the password cannot be seen by someone listening on the network.
ssh automatically maintains and checks a database containing identification for all hosts it has ever been used with. Host keys are stored in ~/.ssh/known_hosts in the user’s home directory. Additionally, the file /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts is automatically checked for known hosts. Any new hosts are automatically added to the user’s file. If a host’s identification ever changes, ssh warns about this and disables password authentication to prevent server spoofing or man-in-the-middle attacks, which could otherwise be used to circumvent the encryption. The StrictHostKeyChecking option can be used to control logins to machines whose host key is not known or has changed.
When the user’s identity has been accepted by the server, the server either executes the given command in a non-interactive session or, if no command has been specified, logs into the machine and gives the user a normal shell as an interactive session. All communication with the remote command or shell will be automatically encrypted.
If an interactive session is requested ssh by default will only request a pseudo-terminal (pty) for interactive sessions when the client has one. The flags -T and -t can be used to override this behaviour.
If a pseudo-terminal has been allocated the user may use the escape characters noted below.
If no pseudo-terminal has been allocated, the session is transparent and can be used to reliably transfer binary data. On most systems, setting the escape character to “none” will also make the session transparent even if a tty is used.
The session terminates when the command or shell on the remote machine exits and all X11 and TCP connections have been closed.
When a pseudo-terminal has been requested, ssh supports a number of functions through the use of an escape character.
A single tilde character can be sent as ~~ or by following the tilde by a character other than those described below. The escape character must always follow a newline to be interpreted as special. The escape character can be changed in configuration files using theEscapeChar configuration directive or on the command line by the -e option.
The supported escapes (assuming the default ‘~’) are:
Forwarding of arbitrary TCP connections over the secure channel can be specified either on the command line or in a configuration file. One possible application of TCP forwarding is a secure connection to a mail server; another is going through firewalls.
In the example below, we look at encrypting communication between an IRC client and server, even though the IRC server does not directly support encrypted communications. This works as follows: the user connects to the remote host using ssh, specifying a port to be used to forward connections to the remote server. After that it is possible to start the service which is to be encrypted on the client machine, connecting to the same local port, and sshwill encrypt and forward the connection.
The following example tunnels an IRC session from client machine “127.0.0.1” (localhost) to remote server “server.example.com”:
$ ssh -f -L 1234:localhost:6667 server.example.com sleep 10 $ irc -c '#users' -p 1234 pinky 127.0.0.1
This tunnels a connection to IRC server “server.example.com”, joining channel “#users”, nickname “pinky”, using port 1234. It doesn’t matter which port is used, as long as it’s greater than 1023 (remember, only root can open sockets on privileged ports) and doesn’t conflict with any ports already in use. The connection is forwarded to port 6667 on the remote server, since that’s the standard port for IRC services.
The -f option backgrounds ssh and the remote command “sleep 10” is specified to allow an amount of time (10 seconds, in the example) to start the service which is to be tunnelled. If no connections are made within the time specified, ssh will exit.
If the ForwardX11 variable is set to “yes” (or see the description of the -X, -x, and -Y options above) and the user is using X11 (the DISPLAY environment variable is set), the connection to the X11 display is automatically forwarded to the remote side in such a way that any X11 programs started from the shell (or command) will go through the encrypted channel, and the connection to the real X server will be made from the local machine. The user should not manually set DISPLAY. Forwarding of X11 connections can be configured on the command line or in configuration files.
The DISPLAY value set by ssh will point to the server machine, but with a display number greater than zero. This is normal, and happens because ssh creates a “proxy” X server on the server machine for forwarding the connections over the encrypted channel.
ssh will also automatically set up Xauthority data on the server machine. For this purpose, it will generate a random authorization cookie, store it in Xauthority on the server, and verify that any forwarded connections carry this cookie and replace it by the real cookie when the connection is opened. The real authentication cookie is never sent to the server machine (and no cookies are sent in the plain).
If the ForwardAgent variable is set to “yes” (or see the description of the -A and -a options above) and the user is using an authentication agent, the connection to the agent is automatically forwarded to the remote side.
When connecting to a server for the first time, a fingerprint of the server’s public key is presented to the user (unless the option StrictHostKeyChecking has been disabled). Fingerprints can be determined using ssh-keygen(1):
$ ssh-keygen -l -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_keyIf the fingerprint is already known, it can be matched and the key can be accepted or rejected. If only legacy (MD5) fingerprints for the server are available, the ssh-keygen(1) -Eoption may be used to downgrade the fingerprint algorithm to match.
Because of the difficulty of comparing host keys just by looking at fingerprint strings, there is also support to compare host keys visually, using random art. By setting the VisualHostKeyoption to “yes”, a small ASCII graphic gets displayed on every login to a server, no matter if the session itself is interactive or not. By learning the pattern a known server produces, a user can easily find out that the host key has changed when a completely different pattern is displayed. Because these patterns are not unambiguous however, a pattern that looks similar to the pattern remembered only gives a good probability that the host key is the same, not guaranteed proof.
To get a listing of the fingerprints along with their random art for all known hosts, the following command line can be used:
$ ssh-keygen -lv -f ~/.ssh/known_hostsIf the fingerprint is unknown, an alternative method of verification is available: SSH fingerprints verified by DNS. An additional resource record (RR), SSHFP, is added to a zonefile and the connecting client is able to match the fingerprint with that of the key presented.
In this example, we are connecting a client to a server, “host.example.com”. The SSHFP resource records should first be added to the zonefile for host.example.com:
$ ssh-keygen -r host.example.com.
The output lines will have to be added to the zonefile. To check that the zone is answering fingerprint queries:
$ dig -t SSHFP host.example.comFinally the client connects:
$ ssh -o "VerifyHostKeyDNS ask" host.example.com [...] Matching host key fingerprint found in DNS. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
See the VerifyHostKeyDNS option in ssh_config(5) for more information.
ssh contains support for Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnelling using the tun(4) network pseudo-device, allowing two networks to be joined securely. The sshd_config(5)configuration option PermitTunnel controls whether the server supports this, and at what level (layer 2 or 3 traffic).
The following example would connect client network 10.0.50.0/24 with remote network 10.0.99.0/24 using a point-to-point connection from 10.1.1.1 to 10.1.1.2, provided that the SSH server running on the gateway to the remote network, at 192.168.1.15, allows it.
On the client:
# ssh -f -w 0:1 192.168.1.15 true # ifconfig tun0 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.252 # route add 10.0.99.0/24 10.1.1.2
On the server:
# ifconfig tun1 10.1.1.2 10.1.1.1 netmask 255.255.255.252 # route add 10.0.50.0/24 10.1.1.1
Client access may be more finely tuned via the /root/.ssh/authorized_keys file (see below) and the PermitRootLogin server option. The following entry would permit connections ontun(4) device 1 from user “jane” and on tun device 2 from user “john”, if PermitRootLogin is set to “forced-commands-only”:
tunnel="1",command="sh /etc/netstart tun1" ssh-rsa ... jane tunnel="2",command="sh /etc/netstart tun2" ssh-rsa ... john
Since an SSH-based setup entails a fair amount of overhead, it may be more suited to temporary setups, such as for wireless VPNs. More permanent VPNs are better provided by tools such as ipsecctl(8) and isakmpd(8).
ssh will normally set the following environment variables:
DISPLAYDISPLAY variable indicates the location of the X11 server. It is automatically set by ssh to point to a value of the form “hostname:n”, where “hostname” indicates the host where the shell runs, and ‘n’ is an integer ≥ 1. ssh uses this special value to forward X11 connections over the secure channel. The user should normally not set DISPLAY explicitly, as that will render the X11 connection insecure (and will require the user to manually copy any required authorization cookies).HOMELOGNAMEUSER; set for compatibility with systems that use this variable.MAILPATHPATH, as specified when compiling ssh.SSH_ASKPASSDISPLAY andSSH_ASKPASS are set, it will execute the program specified by SSH_ASKPASS and open an X11 window to read the passphrase. This is particularly useful when calling ssh from a .xsession or related script. (Note that on some machines it may be necessary to redirect the input from /dev/null to make this work.)SSH_AUTH_SOCKSSH_CONNECTIONSSH_ORIGINAL_COMMANDSSH_TTYSSH_TUNNELSSH_USER_AUTHTZUSERAdditionally, ssh reads ~/.ssh/environment, and adds lines of the format “VARNAME=value” to the environment if the file exists and users are allowed to change their environment. For more information, see the PermitUserEnvironment option in sshd_config(5).
ssh exits with the exit status of the remote command or with 255 if an error occurred.
scp(1), sftp(1), ssh-add(1), ssh-agent(1), ssh-keygen(1), ssh-keyscan(1), tun(4),ssh_config(5), ssh-keysign(8), sshd(8)
S. Lehtinen and C. Lonvick, The Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol Assigned Numbers, RFC 4250,January 2006.
T. Ylonen and C. Lonvick, The Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol Architecture, RFC 4251, January 2006.
T. Ylonen and C. Lonvick, The Secure Shell (SSH) Authentication Protocol, RFC 4252,January 2006.
T. Ylonen and C. Lonvick, The Secure Shell (SSH) Transport Layer Protocol, RFC 4253,January 2006.
T. Ylonen and C. Lonvick, The Secure Shell (SSH) Connection Protocol, RFC 4254, January 2006.
J. Schlyter and W. Griffin, Using DNS to Securely Publish Secure Shell (SSH) Key Fingerprints, RFC 4255, January 2006.
F. Cusack and M. Forssen, Generic Message Exchange Authentication for the Secure Shell Protocol (SSH), RFC 4256, January 2006.
J. Galbraith and P. Remaker, The Secure Shell (SSH) Session Channel Break Extension, RFC 4335, January 2006.
M. Bellare, T. Kohno, and C. Namprempre, The Secure Shell (SSH) Transport Layer Encryption Modes, RFC 4344, January 2006.
B. Harris, Improved Arcfour Modes for the Secure Shell (SSH) Transport Layer Protocol, RFC 4345, January 2006.
M. Friedl, N. Provos, and W. Simpson, Diffie-Hellman Group Exchange for the Secure Shell (SSH) Transport Layer Protocol, RFC 4419, March 2006.
J. Galbraith and R. Thayer, The Secure Shell (SSH) Public Key File Format, RFC 4716,November 2006.
D. Stebila and J. Green, Elliptic Curve Algorithm Integration in the Secure Shell Transport Layer, RFC 5656, December 2009.
A. Perrig and D. Song, Hash Visualization: a New Technique to improve Real-World Security,1999, International Workshop on Cryptographic Techniques and E-Commerce (CrypTEC ’99).
OpenSSH is a derivative of the original and free ssh 1.2.12 release by Tatu Ylonen. Aaron Campbell, Bob Beck, Markus Friedl, Niels Provos, Theo de Raadt and Dug Song removed many bugs, re-added newer features and created OpenSSH. Markus Friedl contributed the support for SSH protocol versions 1.5 and 2.0.
防火墙 常用方法:
来自:https://www.cnblogs.com/freedomwei/p/10851455.html
1.firewall的基本启动/停止/重启命令 #centos7启动防火墙 systemctl start firewalld.service #centos7停止防火墙/关闭防火墙 systemctl stop firewalld.service #centos7重启防火墙 systemctl restart firewalld.service #设置开机启用防火墙 systemctl enable firewalld.service #设置开机不启动防火墙 systemctl disable firewalld.service 2.新增开放一个端口号 firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent #说明: #–zone #作用域 #–add-port=80/tcp #添加端口,格式为:端口/通讯协议 #–permanent 永久生效,没有此参数重启后失效 #多个端口: firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80-90/tcp --permanent 注意:新增/删除操作需要重启防火墙服务. 其他PC telnet开放的端口必须保证本地 telnet 127.0.0.1 端口号 能通。本地不通不一定是防火墙的问题。 查看本机已经启用的监听端口: #centos7以下使用netstat -ant,7使用ss ss -ant 3.查看 #centos7查看防火墙所有信息 firewall-cmd --list-all #centos7查看防火墙开放的端口信息 firewall-cmd --list-ports 4.删除 #删除 firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp --permanent 注意:新增/删除操作需要重启防火墙服务. (防火墙开放指定端口和协议) firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=12888/tcp firewall-cmd --reload (防火墙屏蔽指定ip地址) firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family='ipv4' source address='128.128.128.128' reject"
以下内容转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/adamas21/p/6241974.html
学习apache安装的时候需要打开80端口,由于centos 7版本以后默认使用firewalld后,网上关于iptables的设置方法已经不管用了,想着反正iptable也不会用,索性直接搬官方文档,学习firewalld了,好像比iptables要简单点了。
2、安装firewalld
root执行 # yum install firewalld firewall-config
3、运行、停止、禁用firewalld
启动:# systemctl start firewalld
查看状态:# systemctl status firewalld 或者 firewall-cmd --state
停止:# systemctl disable firewalld
禁用:# systemctl stop firewalld
4、配置firewalld
查看版本:$ firewall-cmd --version
查看帮助:$ firewall-cmd --help
查看设置:
显示状态:$ firewall-cmd --state
查看区域信息: $ firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
查看指定接口所属区域:$ firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=eth0
拒绝所有包:# firewall-cmd --panic-on
取消拒绝状态:# firewall-cmd --panic-off
查看是否拒绝:$ firewall-cmd --query-panic
更新防火墙规则:# firewall-cmd --reload
# firewall-cmd --complete-reload
两者的区别就是第一个无需断开连接,就是firewalld特性之一动态添加规则,第二个需要断开连接,类似重启服务
将接口添加到区域,默认接口都在public
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-interface=eth0
永久生效再加上 --permanent 然后reload防火墙
设置默认接口区域
# firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=public
立即生效无需重启
打开端口(貌似这个才最常用)
查看所有打开的端口:
# firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --list-ports
加入一个端口到区域:
# firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --add-port=8080/tcp
若要永久生效方法同上
打开一个服务,类似于将端口可视化,服务需要在配置文件中添加,/etc/firewalld 目录下有services文件夹,这个不详细说了,详情参考文档
# firewall-cmd --zone=work --add-service=smtp
移除服务
# firewall-cmd --zone=work --remove-service=smtp
### firewall-cmd see open ports sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=5000/tcp. sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=4990-4999/udp. sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --list-ports
使用方法: [code language="css"] your code here [/code]
The language (or lang) parameter controls how the code is syntax highlighted. The following languages are supported:高亮插件支持的语言有如下
actionscript3
bash
clojure
coldfusion
cpp
csharp
css
delphi
diff
erlang
fsharp
go
groovy
html
java
javafx
javascript
latex (you can also render LaTeX)
matlab (keywords only)
objc
perl
php
powershell
python
r
ruby
scala
sql
text
vb
xml
If the language parameter is not set, it will default to “text” (no syntax highlighting).
Code in between the source code tags will automatically be encoded for display, you don’t need to worry about HTML entities or anything.
可视化操作
<!-- 古登堡编辑器,wordpress 5.0后 就采用这个了 --> <?php> asd </php>
error: rpmdb: BDB0113 Thread/process 1502/140515876947776 failed: BDB1507 Thread died in Berkeley DB library error: db5 error(-30973) from dbenv->failchk: BDB0087 DB_RUNRECOVERY: Fatal error, run database recovery error: cannot open Packages index using db5 - (-30973) error: cannot open Packages database in /var/lib/rpm CRITICAL:yum.main: Error: rpmdb open failed
这个问题好奇怪啊,之前几天 登入服务器,跟我说 yum 出了问题。
今天登入 服务器,跟我说,yum 可以用了。可能是 最近CPU 漏洞的原因吧,
服务器厂商在打补丁吧,反正现在能用了,以前好好的突然报出这个问题 我也觉得是挺奇怪的。现在能用了就好。
故障描述:今天下午测试OpenStack,在使用yum安装一个包的时候,手欠了下,结果被我终止了,如是有了下面的记录
先清空下缓存,发现rpmdb open failed
[bash]
[root@linux-node1 glance]# yum clean all
error: rpmdb: BDB0113 Thread/process 21357/140557926295360 failed: BDB1507 Thread died in Berkeley DB library
error: db5 error(-30973) from dbenv->failchk: BDB0087 DB_RUNRECOVERY: Fatal error, run database recovery
error: cannot open Packages index using db5 – (-30973)
CRITICAL:yum.main:
Error: rpmdb open failed
[/bash]
然后试了下yum makecache,问题仍旧不能解决
[bash]
[root@linux-node1 glance]# yum makecache
error: rpmdb: BDB0113 Thread/process 21357/140557926295360 failed: BDB1507 Thread died in Berkeley DB library
error: db5 error(-30973) from dbenv->failchk: BDB0087 DB_RUNRECOVERY: Fatal error, run database recovery
error: cannot open Packages index using db5 – (-30973)
error: cannot open Packages database in /var/lib/rpm
CRITICAL:yum.main:
Error: rpmdb open failed
[/bash]
解决方法:
[bash]
[root@linux-node1 glance]# ls /var/lib/rpm/
Basenames __db.001 __db.003 Dirnames Installtid Obsoletename Providename .rpm.lock Sigmd5
Conflictname __db.002 .dbenv.lock Group Name Packages Requirename Sha1header Triggername
[root@linux-node1 glance]# rm -f /var/lib/rpm/__db*
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
[root@linux-node1 glance]# rpm –rebuilddb
[root@linux-node1 glance]# yum clean all
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks
Cleaning repos: base centos-ceph-hammer centos-openstack-mitaka centos-qemu-ev epel extras updates
Cleaning up everything
Cleaning up list of fastest mirrors<span data-mce-type="bookmark" style="display: inline-block; width: 0px; overflow: hidden; line-height: 0;" class="mce_SELRES_end"></span>
[/bash]
问题得到解决 (下面是 另一种 代码风格 展示)
[root@linux-node1 glance]# ls /var/lib/rpm/ Basenames __db.001 __db.003 Dirnames Installtid Obsoletename Providename .rpm.lock Sigmd5 Conflictname __db.002 .dbenv.lock Group Name Packages Requirename Sha1header Triggername [root@linux-node1 glance]# rm -f /var/lib/rpm/__db* You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root [root@linux-node1 glance]# rpm --rebuilddb [root@linux-node1 glance]# yum clean all Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Cleaning repos: base centos-ceph-hammer centos-openstack-mitaka centos-qemu-ev epel extras updates Cleaning up everything Cleaning up list of fastest mirrors
转自:http://blog.51cto.com/molewan/1906370
谷歌快照历史遗留:centos7安装nginx,mysql,php
centos7安装nginx
cnetos7安装php
centos7安装mysql
在管理进程时通常要借助一些工具,比较常用的就是ps和top了;不过CentOS还为我们提供了一个更加强大的工具htop,下面就来了解一下此工具的使用方法。
htop工具在epel源中提供,请自行配置epel源,也可以直接下载htop的源码包进行安装。
htop跟top一样,也是打开一个实时的监控界面,直接输入htop命令打开如下图所示界面:
在上图中将输出的界面划分成了四个区域,其中:
上左区:显示了CPU、物理内存和交换分区的信息;
上右区:显示了任务数量、平均负载和连接运行时间等信息;
进程区域:显示出当前系统中的所有进程;
操作提示区:显示了当前界面中F1-F10功能键中定义的快捷功能。
F1:显示帮助信息;
F2:配置界面中的显示信息;
我们可以根据自己的需要修改显式模式以及想要显示的内容,比如:以LED的形式显示CPU的使用情况,并且在左边的区域添加hostname,在右边的区区域添加clock;
我们也可以自定义进程区域中的显示内容:
F4:进程过滤器;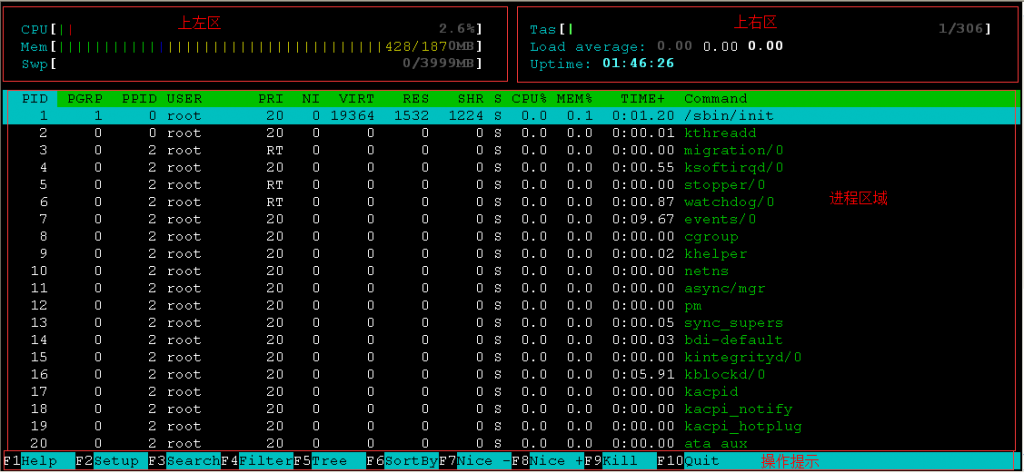 从上面的结果可以看出search和filter的区别:
从上面的结果可以看出search和filter的区别:
search会将光标定位到符合条件的进程上,通过F3键进行逐个查找;而filter会直接将符合条件的进程筛选出来。
search和filter都使用ESC键来取消功能。
F7:减小nice值;
F8:增加nice值;
直接修改光标选取的进程的nice值:
F10:退出htop。
空格键:用于标记选中的进程,用于实现对多个进程同时操作;
U:取消所有选中的进程;
s:显示光标所在进程执行的系统调用;
下面显示的为init的系统调用信息:
l:显示光标所在进程的文件列表;
I:对排序的结果进行反转显示;
例如,对PPID进行排序后,按‘I’键将会对PPID的排序结果进行反向排序。
a:绑定进程到指定的CPU;
u:显示指定用户的进程;
P:按照CPU使用百分比排序,对应CPU%列;
T:按照进程运行的时间排序,对应TIME+列;
K:隐藏内核线程;
H:隐藏用户线程;
#:快速定位光标到PID所指定的进程上。
-d:设置刷新时间,单位为秒;
-C:设置界面为无颜色;
-u:显示指定用户的进程;
[root@testdb ~]#htop -u test1
-s:以指定的列排序;
[root@testdb ~]#htop -s PPID
转载自:http://www.178linux.com/4394
作者:petmaster